Watch this video to make this project (తెలుగులో )
Watch this video to make this project (In English)
Step 1: Downloading and Installing the Blynk App on the Smartphone
Blynk is a Platform with IOS and Android apps to control Arduino, Raspberry Pi etc over the Internet. It’s a digital dashboard where you can build a graphic interface for your project by simply dragging and dropping widgets.
1)Open Play store and download and install the Blynk App.
2)Once the app is installed either login to it using Facebook or create a new account on Blynk and login using that.
3)After logging in, create a new project by clicking ‘New Project’.
4)Give the project a name of your liking. Select the hardware device as NodeMCU and select the connection type as WIFI, and click on create.
5)At this point Blynk will send an Auth token to your email id. We will use this ‘Auth token’ to link our app with the NodeMCU. (This process will be done in later stages)
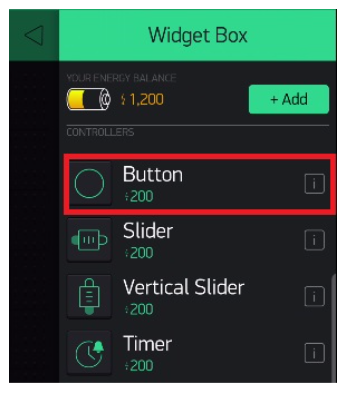
6)To add a new button just click anywhere on the blank area and select button from the side menu that pops up. You can place the button anywhere on the screen.
7)Click on the Button and give it a name.
Step 2: Downloading Arduino IDE and Configuring Blynk Libraries
1)Now let’s install the Arduino IDE. Go to the below link and download the IDE for your preferred operating system.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software
2)You’ll also need to install the Blynk Arduino Library, which helps generate the firmware running on your ESP8266. Blynk Library establishes communication between your hardware, Blynk Cloud and Blynk Apps.
There are three ways to install Blynk Library for Arduino IDE:
To install a new library into your Arduino IDE you can use the Library Manager (available from IDE version 1.6.2). Open the IDE and click on the "Sketch" menu and then Include Library > Manage Libraries.
Then the Library Manager will open and you will find a list of libraries that are already installed or ready for installation. Search for Blynk library and in the version selection choose the latest version to date

Finally click on Install and wait for the IDE to install the new library. Downloading may take time depending on your connection speed. Once it has finished, an Installed tag should appear next to the Bridge library. You can close the library manager.
You can now find the new library available in the Sketch > Include Library menu.
2. Install Blynk as ZIP file in Arduino IDE
Blynk library is available as a downloadable ZIP. Starting with Arduino IDE version 1.0.5, you can install 3rd party libraries in the IDE.
Download Blynk Library by clicking the link here
https://github.com/blynkkk/blynk-library/releases/tag/v0.6.1
☝️Do not unzip the downloaded library, leave it as is.
In the Arduino IDE, navigate to Sketch > Include Library > Add .ZIP Library. At the top of the drop down list, select the option to "Add .ZIP Library''.
1)Open Play store and download and install the Blynk App.
2)Once the app is installed either login to it using Facebook or create a new account on Blynk and login using that.
3)After logging in, create a new project by clicking ‘New Project’.
4)Give the project a name of your liking. Select the hardware device as NodeMCU and select the connection type as WIFI, and click on create.
5)At this point Blynk will send an Auth token to your email id. We will use this ‘Auth token’ to link our app with the NodeMCU. (This process will be done in later stages)
6)To add a new button just click anywhere on the blank area and select button from the side menu that pops up. You can place the button anywhere on the screen.
7)Click on the Button and give it a name.
Step 2: Downloading Arduino IDE and Configuring Blynk Libraries
1)Now let’s install the Arduino IDE. Go to the below link and download the IDE for your preferred operating system.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software
2)You’ll also need to install the Blynk Arduino Library, which helps generate the firmware running on your ESP8266. Blynk Library establishes communication between your hardware, Blynk Cloud and Blynk Apps.
There are three ways to install Blynk Library for Arduino IDE:
- Using built-in library manager in Arduino IDE
or - Installing Blynk library as ZIP file in Arduino IDE
or - Manually install Blynk Library
you can follow any one method to install Blynk Library for Arduino IDE
To install a new library into your Arduino IDE you can use the Library Manager (available from IDE version 1.6.2). Open the IDE and click on the "Sketch" menu and then Include Library > Manage Libraries.

Then the Library Manager will open and you will find a list of libraries that are already installed or ready for installation. Search for Blynk library and in the version selection choose the latest version to date

Finally click on Install and wait for the IDE to install the new library. Downloading may take time depending on your connection speed. Once it has finished, an Installed tag should appear next to the Bridge library. You can close the library manager.
You can now find the new library available in the Sketch > Include Library menu.
2. Install Blynk as ZIP file in Arduino IDE
Blynk library is available as a downloadable ZIP. Starting with Arduino IDE version 1.0.5, you can install 3rd party libraries in the IDE.
Download Blynk Library by clicking the link here
https://github.com/blynkkk/blynk-library/releases/tag/v0.6.1
☝️Do not unzip the downloaded library, leave it as is.
In the Arduino IDE, navigate to Sketch > Include Library > Add .ZIP Library. At the top of the drop down list, select the option to "Add .ZIP Library''.
Return to the Sketch > Include Library menu. menu. You should now see the library at the bottom of the drop-down menu. It is ready to be used in your sketch. The zip file will have been expanded in the libraries folder in your Arduino sketches directory.
The Library will be available to use in sketches, but with older IDE versions examples for the library will not be exposed in the File > Examples until after the IDE has restarted.
3. Install Blynk library manuallyDownload the latest Blynk_Release_vXX.zip file from the GitHub page using the link
https://github.com/blynkkk/blynk-library/releases/tag/v0.6.1
Unzip the Blynk_Release_vXX.zip archive. You will notice that archive contains several folders and several libraries.
Copy all of these libraries to your sketchbook folder of Arduino IDE.
To find the location of your sketchbook folder, go to top menu in Arduino IDE:
Windows: File → Preferences
Mac OS: Arduino → Preferences
The structure of your your sketchbook folder should now look like this, along with your other sketches (if you have them):
your_sketchbook_folder/libraries/Blynk your_sketchbook_folder/libraries/BlynkESP8266_Lib ... your_sketchbook_folder/tools/BlynkUpdater your_sketchbook_folder/tools/BlynkUsbScript ...
☝️ Note that
libraries should go to libraries
tools should go to tools
If you don't have libraries or tools folders, you can create them manually.
Step 3: Uploading the code to NodeMCU.
Connect the NodeMCU to your PC using a USB cable.
Now, we’ll set up the Arduino IDE by changing some settings. So, open up the Arduino IDE.
Now go to File > Preferences > Additional Boards Manager URLs, and copy this URL
http://arduino.esp8266.com/stable/package_esp8266com_index.json
Now install CP210x USB to UART Bridge VCP Drivers by using below link https://www.silabs.com/products/development-tools/software/usb-to-uart-bridge-vcp-drivers
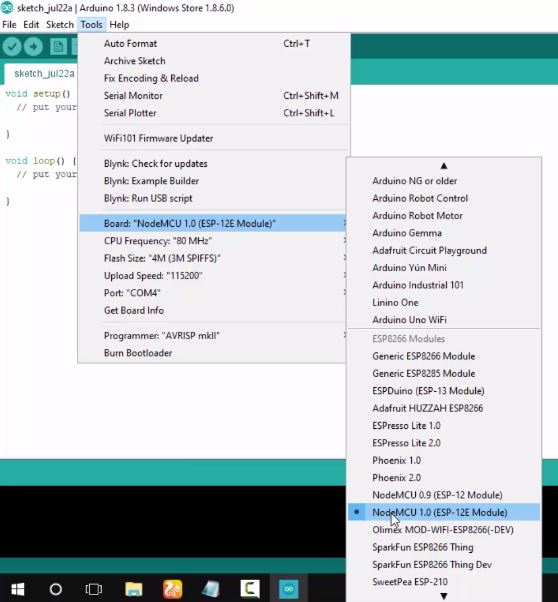
Go to Tools > Port and make sure an appropriate port is selected. In my case it’s COM 4. This is the USB port in which the NodeMCU is connected.
4.Now Go to Tools > Board and select ‘NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)’ as the board. And that’s all the settings we need to change. So now let’s begin writing some code.
5.Go to Files > Examples > Blynk > Boards_WIFI > ESP8266_Standalone. A new file with some prewritten code will open.

6.Now, in this file we only need to change 3 lines of code. Change the line where it says ‘char auth[] = “YourAuthToken”’ and replace the ‘YourAuthToken’ part with your Blynk’s auth token that you received in your email.Change the line where it says ‘char ssid[] = “YourNetworkName”’ and replace the ‘YourNetworkName’ part with the name of your WIFI network that you want your NodeMCU to connect to. In my case the name of my WIFI network is ‘The Network’Change the line where it says ‘char pass[] = “YourPassword”’ and replace the ‘YourPassword’ part with the password of your WIFI network. In my case password of my WIFI network is ‘The Network’ is ‘abcd1234’.
7.That’s really all the code that we need to write! We are now ready to upload this code to the NodeMCU. So directly hit upload button at the top (besides the button that has a checkmark), and wait for it to process.
8)The code will be uploaded to the NodeMCU and the next time you power it on, it will automatically connect to the specified WIFI network.
At this point, we have a fully functional connection between the NodeMCU, Blynk app and our electrical appliances. So, you can directly run your Blynk project from your phone and turn the electrical appliances on or off using the buttons that we created in the app. And if you are satisfied with this and don’t want to connect the NodeMCU with the Google Assistant and control the appliances using voice commands, then you don’t have to read the remaining tutorial and you can stop right here. Otherwise let’s move forward.
Step 5: Connecting Google Assistant (using IFTTT) to make the NodeMCU work with voice commands.
We cannot connect the Google Assistant to the NodeMCU directly, and that is the only reason we are using the Blynk app. Blynk app can directly connect to the NodeMCU and send data to it. So, if we can send the voice commands interpreted by google assistant directly to the Blynk app, the Blynk app can then forward those commands to the NodeMCU. But the problem is Google Assistant cannot directly understand foreign commands like “turn on the fan” or “turn on relay one” etc. on its own. So, to solve this we use another intermediate app/website called ‘IFTTT’.
Simply, to control our home appliances over the internet we are using NodeMCU and to connect NodeMCU with the home appliances we use a relay board. Now to send on or off signals to the NodeMCU we use our smartphone, and we do this using the Blynk app. But we want to send the on or off signals using voice commands. To do this we use google assistant in our smartphone and an app called IFTTT.
So, in the end what will happen is, when we say a voice command like “ok google turn on the light” to the Google Assistant, Google Assistant sends that this foreign command to IFTTT. IFTTT interprets this command and sends an On or Off signal to the Blynk app via the Blynk Server. Blynk will then send this signal to the NodeMCU and then to our electrical appliances.
Enough said, lets configure IFTTT. Go to IFTTT’s website and sign up to it using your Google Account.
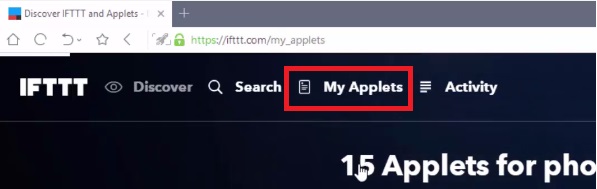
- After Signing in click on My Applets from the header and select New Applet.
2. Click on ‘this’.


6. Next, for the first text box type the phrase that you want to say to Google Assistant. It can be anything such as “Turn on the bulb”, “Turn on the fan” or anything you like.

7. For the next two text boxes, you write some other ways to say the first command. For example, if in the first textbox you wrote “Turn on the bulb”, then in the second and third textboxes you can write something like “Turn the bulb On” or “Please Turn on the bulb”
8. In the fourth text box type the reply that Google Assistant should respond with. For example, “Okay, Turning on the bulb”.
8. In the fourth text box type the reply that Google Assistant should respond with. For example, “Okay, Turning on the bulb”.
10. Now, click on that
11.Type webhooks select it, and click connect. Webhooks will allow us to send commands to the Blynk Server.
12. Now, in the URL field type this URL:
http://188.166.206.43/ YourAuthTokenHere / update / DigitalPinToBeUpdateHere
This is the URL of Blynk Server of India, but it should work for other places as well. Replace the “YourAuthTokenHere” part with your Blynk Auth token that you received in the mail. And “DigitalPinToBeUpdateHere” part with the Digital pin of NodeMCU that is to be updated. So, as we assigned the Digital Pin D3 of NodeMCU to relay one we must write D3 in place of “DigitalPinToBeUpdateHere”. But wait we cannot write D3 there, because when Blynk Server receives this command from IFTTT it assumes as if the command it received was to be sent to an ‘Arduino Uno’ board, but in our case, we are sending it to NodeMCU.
To solve this, we must type the Digital pin of Arduino which corresponds with the NodeMCU. You can find the mapping in the image below.
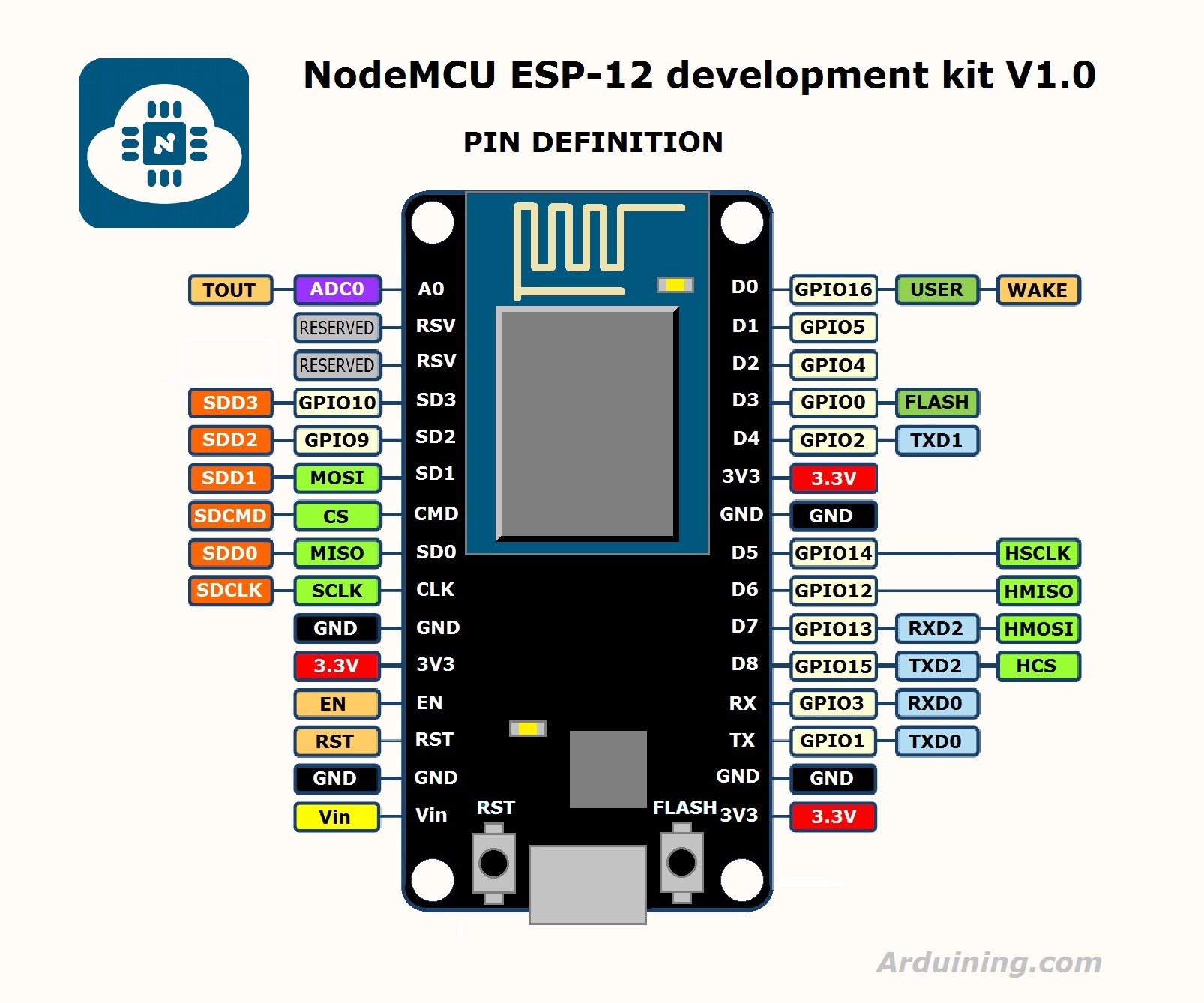
As you can see in the image, Digital Pin D3 of NodeMCU corresponds to Pin D0 of Arduino. So instead of D3, I’ll write D0 as the pin. In the end the URL should look something like this:
http://188.166.206.43/ d5846384ef7140cfg54699bbc97f2ad8 / update / D0
13. Next, Select the ‘Method’ field as PUT
14. Select ‘Content type’ as Application/JSON.
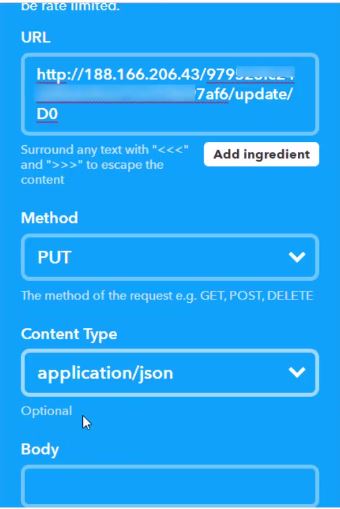

Here ‘0’ means to turn off, so we are basically saying Blynk to turn on relay that is connected to pin D3, which in our case is Relay one.
16. Now click on ‘Create Action’ and then Finish.
Similarly, we create another applet to turn off the relay.
Repeat all the points above from point 5 except the following changes:
In points 6 and 7, instead of writing “Turn on the bulb”, type “Turn off the bulb”
In point 15, instead of [“0”], type [“1”].
So now we have successfully created two triggers to turn on and off one Relay. So Similarly, we create triggers for remaining 3 relays. Just change the phrase and Digital pin for each Relay. All the other steps will remain the same. So, in the end for 4 relays, we should have 8 triggers to turn each of them on or off.
When this is all done, you will be able to say the voice commands to your Google Assistant, So now, you have your own voice controlled.
In points 6 and 7, instead of writing “Turn on the bulb”, type “Turn off the bulb”
In point 15, instead of [“0”], type [“1”].
So now we have successfully created two triggers to turn on and off one Relay. So Similarly, we create triggers for remaining 3 relays. Just change the phrase and Digital pin for each Relay. All the other steps will remain the same. So, in the end for 4 relays, we should have 8 triggers to turn each of them on or off.
When this is all done, you will be able to say the voice commands to your Google Assistant, So now, you have your own voice controlled.